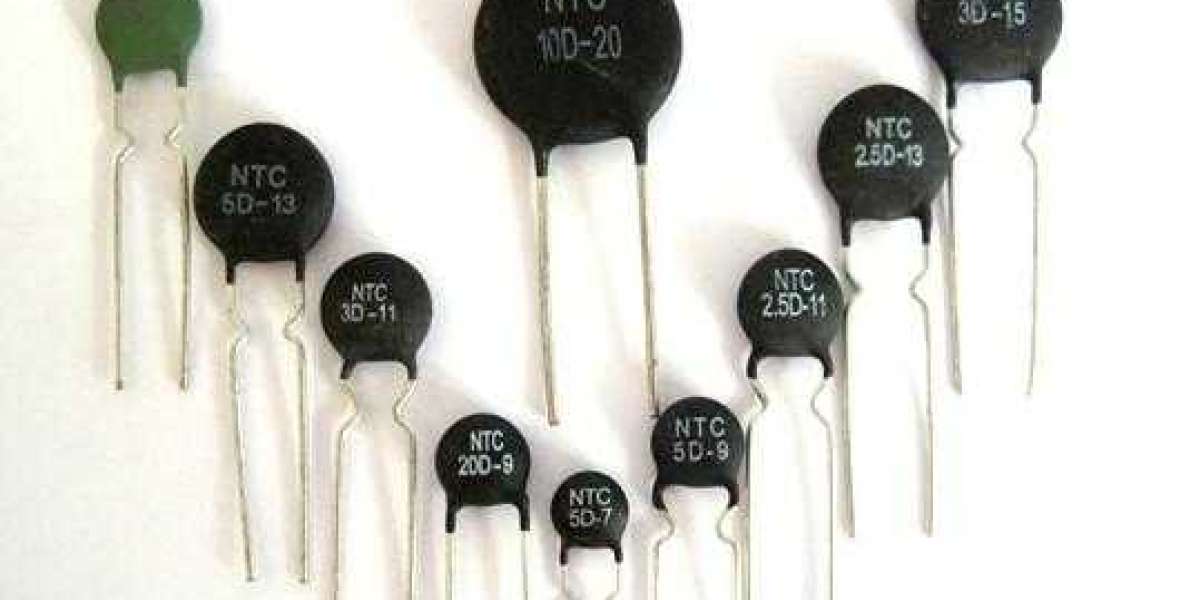
NTC thermistor is a kind of resistance with a negative temperature coefficient. The characteristic of this resistance value is realized to decrease with the increase of temperature, and the material it uses is a semiconductor material with a large negative temperature coefficient. This kind of resistance is widely used in switching power supplies, UPS power supplies, electronic ballasts, temperature sensors, automatic adjustment heaters, and other occasions. This article introduces the three functions of the thermistor in surge absorption, temperature measurement, and temperature compensation.

1. Suppress Surge Current
This type of thermistor resistance is a power type. Although the volume is small, the power is great. This kind of resistance is generally connected in series on the mains input line. Its resistance is very small. Zero power resistance is the most basic parameter of thermal resistors, and manufacturers generally give this parameter. It can effectively suppress the startup surge current. At the same time, it consumes negligible power.
2. Use Temperature Sensor To Measure Temperature
As a thermistor that measures temperature, it uses changes in the outside temperature to change the resistance. Because the NTC resistor will always pass a certain amount of current when it is connected to the circuit. This current causes the NTC to generate heat. When the NTC resistance drops, it will have a great impact on the measurement. Therefore, it is necessary to control the heating degree of the thermistor to avoid excessive current flowing through it to cause the component to heat up and produce measurement errors. We can write all or part of the resistance value corresponding to the temperature into the CPU. In this way, the change in resistance value when the outside temperature changes will be realized as a change in voltage.

ntc thermistor
Using the principle of resistor divider, when the NTC changes, the voltage also changes. Use the A/D port to detect the voltage change, and write all the data needed by the thermistor into the MCU. In this way, different resistance values can correspond to different temperatures.
If the temperature accuracy is higher, we can use NTC resistors with higher accuracy, and at the same time use bridge circuits and amplifiers. The thermistor NT1/NT2 and the resistors R1 and R2 form a bridge circuit. When it produces a temperature difference, the amplifier will output the corresponding signal.

3. Temperature Compensation
Electronic components usually have a certain temperature coefficient, and their output signals will drift with temperature changes, which is called "temperature drift". The temperature compensation method can reduce the temperature drift, offset or reduce the temperature drift of its output to a certain extent. Sensors are widely used in various industrial and agricultural productions. The information that needs to be obtained in the production process must be converted into electrical signals that are easy to transmit and process. However, most of the sensor’s sensitive components use metal or semiconductor materials, and their static characteristics are related to the environment. Temperature is closely related. In actual work, due to the large change in the working environment temperature of the sensor, the thermal output caused by the temperature change will bring about a large measurement error. At the same time, the temperature change also affects the zero point and the sensitivity value and then affects the static characteristics of the sensor. Therefore, measures must be taken to reduce or eliminate the impact of temperature changes, which requires an NTC thermistor to compensate for the temperature of the sensor.